Definition of Dewatering
– Dewatering is the term for the control of groundwater by pumping. -Dewatering process can be defined as pumping from wells or sumps to temporarily lower the groundwater levels to allow excavations to be made in dry and stable conditions below the natural groundwater level.
– Surface water must be controlled as well by collector drains, pumping systems, and French drains to intercept run-off, to avoid the risk of localized flooding and softening of soil exposed in excavation, Surface water can be caused due to rainfall, seepage through cut-off walls, and construction operations ( concreting, washing,..).
Dewatering involves controlling groundwater by pumping, to locally lower groundwater levels in the vicinity of the excavation.
To stop groundwater seepage into the excavation and to ensure stability of excavation side slopes and base it may be necessary to lower groundwater level before the commencement of excavation.
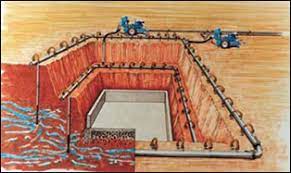
Dewatering is generally done by the following techniques:
– Deep well system
– Well point system

Wellpoint system
Wellpoint dewatering is used for excavations of shallow depths, especially for pipeline trench excavations. In appropriate ground conditions a wellpoint system can be installed speedily and made operational rapidly.


Deepwell system
A deep well system consists of a group of bored wells pumped by submersible pumps. Pumping from each well reduces the groundwater level and creates a cone of depression or drawdown around itself. Several wells acting in combination can lower groundwater levels over a wide area beneath an excavation. The technique can result in large drawdowns, limited only by the depth of the wells, and the hydrogeological conditions.
The wells are generally placed just outside the area of the proposed excavation and are pumped by electric submersible pumps near the base of each well. Water collection pipes, power supply generators, electrical controls, and monitoring systems are located at the surface.
A typical wellpoint system consists of a series of small diameters wells (known as wellpoints) connected via a header pipe, to the suction side of a suitable wellpoint pump. The pump creates a vacuum in the header pipe, drawing water up out of the ground.